Identity Defined Security (IDS) to Safeguard the Digital Realm

Cyber security is a term that has become ubiquitous in today’s digital world. Everyone is aware of the importance and challenges of protecting their data and systems from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. However, not everyone is familiar with one of the most essential and effective aspects of cyber security: Identity Defined Security (IDS)
IDS is a security model that puts identity as a key component of their cyber security strategies. IDS assumes no trust between users, devices, and applications, and verifies every request before granting access. It helps organizations reduce the risk of a breach by combining identity and security solutions, such as identity and access management, privileged access management, endpoint security, network security, and data protection.
Why Identity Defined Security?
The challenges posed by the worldwide pandemic and the need to support a distributed, remote workforce have highlighted the need for improved identity security. The increased use of cloud services and personal devices means more users have the ability to access data from anywhere using systems that may not be under corporate control. Managing access using a traditional perimeter-based approach is no longer feasible. Combined with the prevalence of credential theft, these factors make putting identity at the center of security strategies vital.
Some of the key trends that have seen a recent rise in Identity Defined Security (IDS) solutions:
- The surge of new identities: The proliferation of cloud, mobile, IoT, and other technologies has created a massive increase in the number and types of identities that need to be managed and secured. These include human users, service accounts, bots, devices, applications, APIs, etc. Organizations need to have a comprehensive view and control of these identities and their access rights across different environments.
.png?width=680&height=394&name=Trends%20in%20Identity%20Security%20survey%202023%20(1).png)
- The army of remote workers: The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift to remote work, which poses new challenges for identity and security. Remote workers need secure access to applications and data from anywhere, using any device. Organizations need to ensure that their remote workers have the right level of access, based on their identity, context, and risk. Organizations also need to protect their endpoints from malware and other threats.
- The growth of cloud: The adoption of cloud services and applications has increased the complexity and diversity of the IT landscape. Organizations need to secure their data and resources in the cloud, as well as their hybrid and multi-cloud architectures. Organizations also need to ensure that their cloud providers adhere to the same security standards and regulations as they do.
- New identity-focused cyberattacks: Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics and techniques to exploit the vulnerabilities and gaps in identity and security. Some of the common identity-related attacks include phishing, credential stuffing, password spraying, brute force, ransomware, privilege escalation, lateral movement, etc. Organizations need to detect and prevent these attacks by using advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, behavioral analytics, etc.
.png?width=680&height=378&name=Trends%20in%20Identity%20Security%20survey%202023%20(2).png)
These factors have created a high demand for IDS solutions that can help organizations to secure their digital identities in a dynamic and distributed environment. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global IDS market size is expected to grow from USD 12.5 billion in 2020 to USD 24.1 billion by 2025, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 14.0%
Identity Defined Security Landscape
The IDS landscape varies greatly but it can be broadly classified into these 6 categories below:
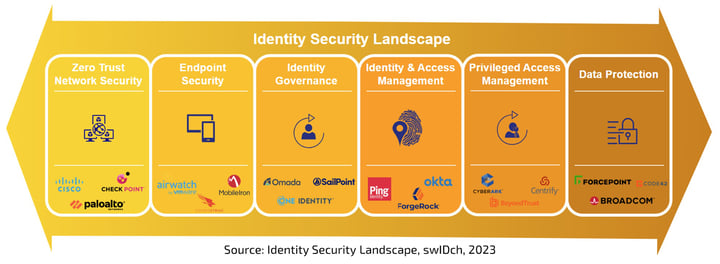
Zero Trust Network Security
Zero Trust Network Security (ZTNS) is a security model that assumes no trust between users, devices, and applications, and verifies every request before granting access. ZTNS aims to reduce the attack surface and prevent unauthorized access by hiding applications from the public internet, enforcing granular policies based on identity and context, and segmenting the network to limit lateral movement. ZTNS looks at 2 keys areas:
- Network security: This protects the network infrastructure and data from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. Network security involves implementing firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), encryption, VPNs, etc., to secure the network perimeter and traffic.
- Cloud security: This secures the data and resources in the cloud, as well as the hybrid and multi-cloud architectures. Cloud security involves implementing cloud access security brokers (CASBs), cloud workload protection platforms (CWPPs), cloud security posture management (CSPM), etc., to protect the cloud environment from threats and vulnerabilities.
Why is ZTNS better than traditional VPNs?
ZTNS can replace VPNs for remote, in-person, and hybrid work environments. VPNs provide broad network protection, but ZTNS is a comprehensive solution that empowers organizations with more granular control.
- Authorization: A VPN verifies users at point of entry to the private corporate network with a login and password. But mature ZTNS solutions perform continuous background monitoring of user and device context to adapt access levels at every connection request.
- Accessibility: When users log in to a VPN, they are granted complete access to the entire network. ZTNS solutions connect authorized users directly to applications rather than to the network—and only to those applications they are authorized to access on need-to-know-based policies.
- Speed: ZTNS solutions are faster than VPNs because they connect users directly to applications rather than sending traffic through a corporate data center. Resources can also be stored on the cloud and don't require a local network, which also leads to faster access.
- Security: ZTNS provides users full access to a network's resources, running the risk of exposing the network. Because ZTNS limits user connections to specific applications and continually verifies user and device trust, zero trust security can better reduce risk and build security resilience than VPNs can.
Endpoint Security

Endpoint security is a way of protecting computer networks from threats that may come from devices that connect to them remotely, such as laptops, smartphones, or tablets. Endpoint security software helps businesses prevent malware and hackers from accessing their data and systems through these devices. Endpoint security is important because it reduces the risk of data breaches, improves network performance, and enables remote working. Some of the key attributes of endpoint security are:
- Antimalware: This is a software that detects and removes malicious programs such as viruses, worms, ransomware, spyware, etc. from the devices. Antimalware can also block malicious websites and downloads, and scan files and emails for threats.
- Attack surface reduction: This is a technique that limits the number of ways that attackers can exploit the devices and the network. Attack surface reduction can include disabling unnecessary services and ports, applying patches and updates, enforcing strong passwords and encryption, and using multi factor authentication.
- Device-based conditional access: This allows businesses to control who can access their network and resources based on the device’s identity and security posture. Device-based conditional access can check if the device is compliant with the security policies, has the latest software versions, and has no malware infections before granting access.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR): This is a capability that monitors the devices for suspicious activities and alerts the security team in real time. EDR can also collect and analyze data from the devices to provide insights into the attack methods, sources, and impacts. EDR can also help with incident response by isolating infected devices, blocking malicious processes, and restoring normal operations.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): This is a framework that combines network and security functions in a cloud-based platform. SASE provides secure access to applications and data regardless of where they are hosted or where the users are located. SASE can also optimize network performance and scalability by using edge computing and software-defined networking.
Identity Governance
Identity governance is a term that refers to the management and protection of digital identities in an organization. It involves ensuring that the right people have the right access to the right resources, and that this access is monitored and audited for security and compliance purposes. Identity governance helps organizations reduce operational costs, mitigate risks, improve compliance, and enhance productivity.
Some of the key aspects of identity governance are:
- Identity lifecycle: This is the process of creating, updating, and deleting user accounts and access rights based on their roles and responsibilities. Identity lifecycle management also involves provisioning and deprovisioning access to applications and data, both on-premises and in the cloud.
- Access lifecycle: This is the process of granting, reviewing, and revoking access to resources based on business needs and policies. Access lifecycle management also involves enforcing granular and role-based access control, verifying user identity and context, and implementing multi factor authentication.
- Separation of Duties (SoD) which is a set of controls that prevent users from having access to conflicting or incompatible resources or tasks. For example, a user who can create and approve purchase orders may have the opportunity to commit fraud or error. SoD policies help to reduce the risk of such scenarios by requiring multiple people to perform a single task or critical steps within a task.
- Approval workflows are the processes that determine whether a user’s request for access to a resource or a role requires approval or not, and who can approve or deny the request. Approval workflows help to ensure that only authorized and appropriate users have access to the resources and roles they need, and that the access is granted in a timely and secure manner. Approval workflows also help to maintain compliance and auditability of the access decisions.
- Audit and compliance: This is the process of monitoring and recording the identity and access activities in the organization for security and regulatory purposes. Audit and compliance also involves generating reports and alerts on any anomalies or violations of the policies and rules.
Identity Governance
Identity governance is a term that refers to the management and protection of digital identities in an organization. It involves ensuring that the right people have the right access to the right resources, and that this access is monitored and audited for security and compliance purposes. Identity governance helps organizations reduce operational costs, mitigate risks, improve compliance, and enhance productivity.
Some of the key aspects of identity governance are:
- Identity lifecycle: This is the process of creating, updating, and deleting user accounts and access rights based on their roles and responsibilities. Identity lifecycle management also involves provisioning and deprovisioning access to applications and data, both on-premises and in the cloud.
- Access lifecycle: This is the process of granting, reviewing, and revoking access to resources based on business needs and policies. Access lifecycle management also involves enforcing granular and role-based access control, verifying user identity and context, and implementing multi factor authentication.
- Separation of Duties (SoD) which is a set of controls that prevent users from having access to conflicting or incompatible resources or tasks. For example, a user who can create and approve purchase orders may have the opportunity to commit fraud or error. SoD policies help to reduce the risk of such scenarios by requiring multiple people to perform a single task or critical steps within a task.
- Approval workflows are the processes that determine whether a user’s request for access to a resource or a role requires approval or not, and who can approve or deny the request. Approval workflows help to ensure that only authorized and appropriate users have access to the resources and roles they need, and that the access is granted in a timely and secure manner. Approval workflows also help to maintain compliance and auditability of the access decisions.
- Audit and compliance: This is the process of monitoring and recording the identity and access activities in the organization for security and regulatory purposes. Audit and compliance also involves generating reports and alerts on any anomalies or violations of the policies and rules.
Identity & Access Management

Identity and access management provides control over user validation and resource access. Commonly known as IAM, this technology ensures that the right people access the right digital resources at the right time and for the right reasons.
- Authentication: This is the process of verifying the identity of a user or device when they try to access a resource or data. Authentication can use different methods, such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, certificates, etc. Sometimes, more than one method is required for extra security, which is called multi factor authentication (MFA).
- Authorization: This is the process of granting or denying access to a resource or data based on the identity and role of the user or device. Authorization can use different models, such as role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), policy-based access control (PBAC), etc. Authorization can also take into account the context and risk of the access request, such as the location, time, device type, etc.
- Risk-based authentication: This is a technique that adjusts the level of authentication required for a user or device based on the risk of the access request. Risk-based authentication can use various factors, such as identity attributes, context, behavior, device type, location, etc., to calculate a risk score and apply appropriate authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, etc.
- Fraud detection: This is a capability that monitors and alerts on any suspicious or anomalous behavior or transactions that may indicate fraud or abuse. Fraud detection can use various techniques, such as rules-based systems, anomaly detection, machine learning, etc., to identify patterns and indicators of fraud. Fraud detection can also help to mitigate the impact of fraud by blocking or reversing fraudulent transactions, notifying users or authorities, or triggering remediation actions.
- Identity Proofing: Identity proofing is the process of verifying and authenticating the identity of a user who wants to access an application or a service. Identity proofing can use different methods and factors, such as personal information, documents, biometrics, or national identity systems, to confirm that the user is who they claim to be. Identity proofing helps to prevent identity fraud and ensure that only authorized and legitimate users can access the resources and data they need.
Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a system that assigns higher permission levels to accounts with access to critical resources and admin-level controls. PAM is based on the principle of least privilege, which is crucial to modern cybersecurity best practices. Some of the key attributes of a PAM are:
- Access control and authorization: This allows organizations to grant or deny access to resources and data based on the identity and role of the user or device. Access control and authorization can use different models, such as role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), policy-based access control (PBAC), etc. Access control and authorization can also take into account the context and risk of the access request, such as the location, time, device type, etc.
- Session monitoring and recording: This enables organizations to track and audit the activities of privileged users and devices during their sessions. Session monitoring and recording can help to detect and prevent unauthorized or malicious actions, such as data theft, system tampering, privilege escalation, etc. Session monitoring and recording can also provide evidence and accountability for compliance and audit purposes.
- Privilege elevation and delegation: This allows organizations to temporarily grant or revoke higher-level privileges to users or devices based on their needs and policies. Privilege elevation and delegation can help to reduce the number of permanent privileged accounts and minimize the exposure of sensitive data and resources. Privilege elevation and delegation can also enable users or devices to perform specific tasks without compromising security or compliance.
- Password management: This helps organizations to manage the passwords of privileged accounts and devices. Password management can include functions such as password rotation, password vaulting, password synchronization, password recovery, etc. Password management can help to prevent password-related attacks, such as credential stuffing, brute force, password spraying, etc., by enforcing strong password policies and practices.
- Compliance and audit reporting: This enables organizations to generate reports and alerts on the identity and access activities of privileged users and devices for security and regulatory purposes. Compliance and audit reporting can help to demonstrate adherence to various standards and regulations by providing visibility and traceability of privileged access management. Compliance and audit reporting can also help to identify and resolve issues, such as policy violations, access anomalies, etc., by using analytics and dashboards.
Data Protection

Data Protection or Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a cybersecurity solution that detects and prevents data breaches, exfiltration, or unwanted destruction of sensitive data. Organizations use DLP to protect and secure their data and comply with regulations. A DLP solution allows organizations to:
- Data discovery and classification: This allows organizations to identify and label the data they have based on its sensitivity and value. Data discovery and classification can help to prioritize the protection of the most critical data and apply appropriate policies and rules.
- Data in motion, at rest, and in use: This enables organizations to monitor and control the data as it travels across the network, as it is stored in various locations, and as it is accessed or processed by users or applications. Data in motion, at rest, and in use can help to prevent data leakage, theft, or loss by blocking or encrypting unauthorized or risky data transfers.
- Policy management and enforcement: This allows organizations to define and implement the rules and actions that govern how the data can be accessed, used, shared, or modified. Policy management and enforcement can help to ensure compliance with various standards and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc., by providing visibility and traceability of data activities.
- Incident response and remediation: This enables organizations to detect and respond to any data incidents or violations that may occur. Incident response and remediation can help to mitigate the impact of data breaches by alerting users or authorities, blocking or reversing data transactions, notifying customers or stakeholders, or triggering remediation actions
Crucial Roles of IDS in Cybersecurity and Identity Management
IDS is important for cyber security because it addresses the challenges and risks that arise from the increasing complexity and diversity of the IT landscape, where traditional security measures based on network perimeters and static credentials are no longer sufficient or effective. IDS helps organizations to protect their data and resources from identity-related attacks, such as phishing, credential stuffing, privilege escalation, etc., by verifying every request before granting access, based on identity attributes and risk factors. IDS also improves user experience, operational efficiency, and compliance by simplifying and automating identity lifecycle management and access provisioning across different environments.
IDS is a vital part of cyber security that enables organizations to secure their digital identities in a dynamic and distributed environment. IDS provides a holistic and adaptive approach to security that leverages the power of identity as a key factor in determining access rights and policies. IDS also supports the evolving needs and demands of the users and the business by providing seamless and secure access to applications and data from anywhere, using any device.
--------------------

Author: Vinny Sagar, Solution Architect, swIDch
With over 15 years of experience in pre-sales, consulting and software development in the Identity and Cyber Security space Vinny has helped many clients across various industries and regions to design and deploy Zero Trust solutions that meet their specific needs and challenges.
--------------------

swIDch will continue its quest to innovate and pioneer next-generation authentication solutions. To stay up-to-date with the latest trends sign up to our newsletter and check out our latest solutions.

In late 2025,a coordinated cyberattack disrupted parts of Poland’s power grid, affectingrenewable energy plants and

Approval has long been treated as a proxy for control. If access is approved, it is assumed to be safe. If the request

At a large industrial site, a contractor needed temporary access to a controller to complete routine maintenance. The
Looking to stay up-to-date with our latest news?